Body Composition
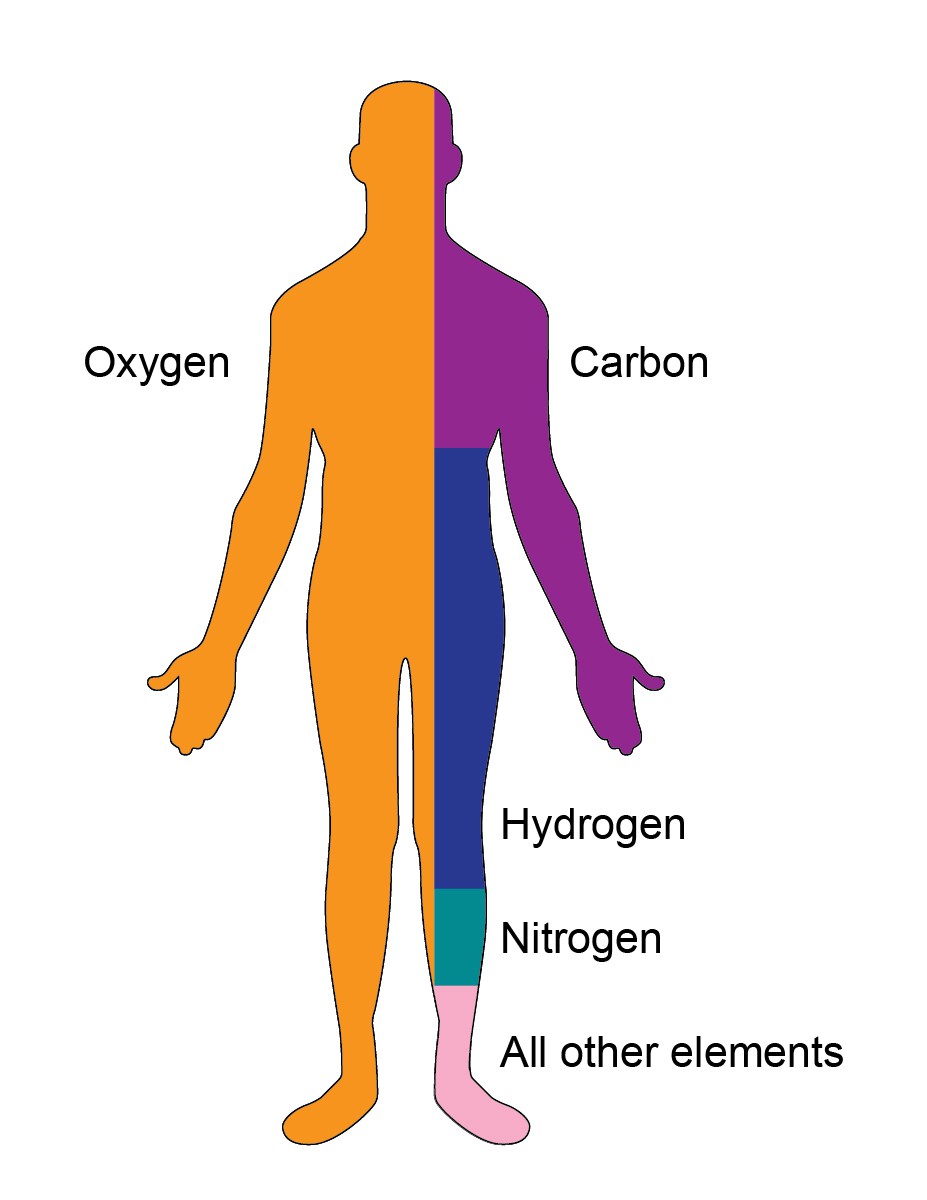
Your body is a fascinating place. Carbon and oxygen are the two most essential elements of the body. The other elements which are present in your body are nitrogen, phosphorous, hydrogen, oxygen, calcium, potassium, sulfur, magnesium, etc.
| ELEMENT | PERCENTAGE IN THE BODY | FUNCTION |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen (O) | 65 | • Primary solvent • Regulate temperature & osmotic pressure |
| Carbon (C) | 18 | • Energy source • Building blocks of the body |
| Hydrogen (H) | 10 | • Present in water and all organic molecules |
| Nitrogen (N) | 3 | • Found in proteins and nucleic acids |
| Calcium (Ca) | 1.5 | • Critical for muscle contraction |
| Phosphorous (P) | 1.0 | • Acts as a buffer • Provides strength and structure to bones and teeth |
| Potassium (K) | 0.35 | • Crucial electrolyte • Helps in transmission of nerve impulse • Regulates heartbeat |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.25 | • Renders shape to the proteins which aid in proper functioning of proteins |
| Sodium (Na) | 0.15 | • Important electrolyte for regulating the amount of water • Helps in nerve signaling |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 0.05 | • Required in more than 300 biochemical reactions • Builds muscle and bones • Chief cofactor in many enzymatic reactions |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.006 | • Help in blood production |
| Copper (Cu), Zinc (Zn), Selenium (Se), Molybdenum (Mb), Fluorine (F), Iodine (I), Manganese (Mn), Cobalt (Co) | Total is less than 0.70 | • Copper is a micronutrient for the growth and development, and also essential for various metabolic functions • Zinc plays an important role in cell growth, cell division, wound healing, and the breakdown of carbohydrates • Selenium protects the body from oxidative damage • Molybdenum removes toxins from metabolism of sulfur containing amino acids • Fluorine is responsible for mineralization and formation of tooth enamel • Iodine is essential for formation of thyroid hormones • Manganese helps in the formation of connective tissues, bones, blood-clotting factors, sex hormones in addition to being critical in fat and carbohydrate metabolism, calcium absorption, and blood sugar regulation |
| Lithium (Li), Strontium (Sr), Aluminium (Al), Silicon (Si), Lead (Pb), Arsenic (As), Vanadium (V), Bromine (Br) | Present in trace amounts | • Lithium is essential for maintaining neurological health • Strontium aids in bone formation and prevent bone loss; the radioactive form of strontium can also kill some cancer cells • Aluminum is responsible for chromatin compaction • Silicon helps in promoting firmness and strength in arteries, connective tissues, tendons, skin, and eyes • Vanadium plays a role in metabolizing enzymes |

No comments:
Post a Comment